Enabling discovery and access to sensitive data across national boundaries is vital for improving human health. It enables more powerful and efficient research by increasing the volume and diversity of data available for analysis. It allows us to better understand the causes of diseases – cancer, rare diseases, infectious diseases like COVID-19 – and develop new medicines and treatments.
Sensitive human omics data are typically generated by research initiatives and shared using specialist repositories which provide services for data submission, discovery, and access. The EGA is one such repository. Established in 2008 at EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in the UK, since 2012 the EGA (“Central EGA”) has been jointly managed by EMBL-EBI and the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Spain.
Many countries have emerging personalised medicine programmes which generate data from national initiatives. These programmes are driving a transition in human genomics from being research-driven to receiving funding through healthcare. Data generated in a clinical context are subject to stricter governance than research data and must follow national data protection legislation.
To solve these challenges, the Federated EGA provides a network of connected resources to enable transnational discovery of and access to human omics data for research, while also respecting jurisdictional data protection regulations. In this way, the Federated EGA infrastructure supports the goals of European initiatives such as the 1+ Million Genomes initiative (1+MG), the European Health Data Space, and a number of EU-funded 1+MG implementation projects including Beyond 1 Million Genomes.
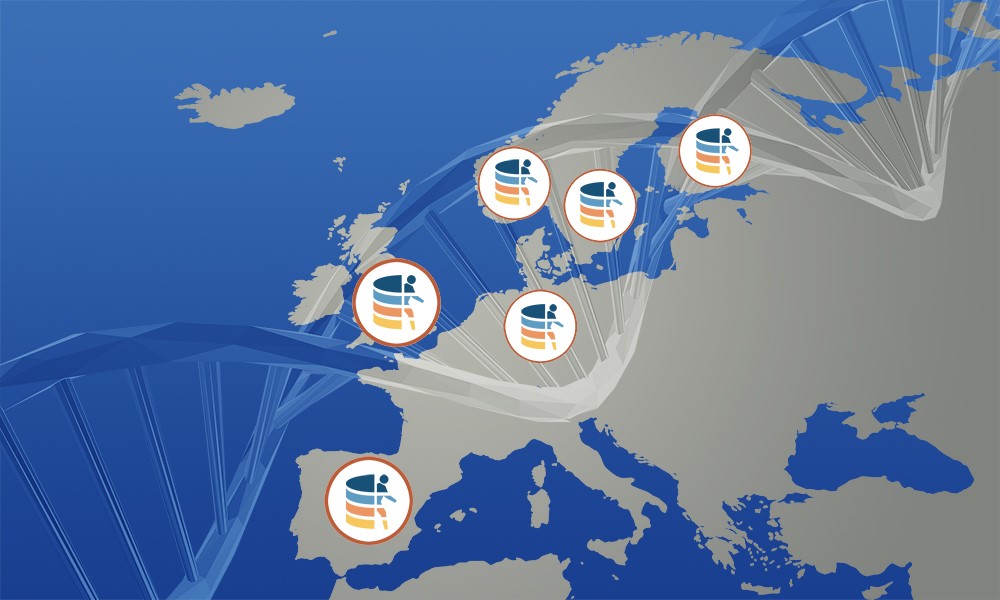
The Federated EGA is made up of “Nodes” – typically nationally funded and operated – which store and manage data locally while allowing global discovery within the Federated EGA network. Since 2016, multiple parallel efforts, supported by ELIXIR and other transnational and national initiatives, have created technical and legal frameworks for establishing the Federated EGA. In 2022, the first five Nodes – Finland, Germany, Norway, Spain, and Sweden – officially joined the Federated EGA by signing Federated EGA Collaboration Agreements with Central EGA.
The Finnish FEGA Node is operated by CSC - IT Center for Science and provides data management services according to national laws and the requirements of the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These services provide tools and support for the whole life-cycle of sensitive research data from collating to analysis, publication, and authorised re-use. The development of the services has been a joint effort with the other Nordic nodes within NeIC's Tryggve and Heilsa projects, and funded by Finnish Ministry of Education and Culture and projects coordinated by ELIXIR Finland. Read more about Finnish FEGA signing.
The German Human Genome-Phenome Archive (GHGA) strives to provide a national infrastructure as well as an ethical and legal framework that balances FAIR omics data usage and data protection needs for Germany. As a Germany-wide consortium funded by the German Research Foundation under the umbrella of the NFDI association, GHGA combines the expertise of 21 universities and research institutions to form a federated national infrastructure. Read more about GHGA signing.
The German Human Genome-Phenome Archive (GHGA) strives to provide a national infrastructure as well as an ethical and legal framework that balances FAIR omics data usage and data protection needs for Germany. As a Germany-wide consortium funded by the German Research Foundation under the umbrella of the NFDI association, GHGA combines the expertise of 21 universities and research institutions to form a federated national infrastructure. Read more about GHGA signing.
In Norway, a key component of the infrastructure is the services of The Sensitive Data Service (TSD) offered by USIT at University of Oslo. The Federated EGA Norway Node is developed by ELIXIR Norway and operated by the University of Oslo as the responsible legal entity. Core software modules are developed jointly with the other Nordic nodes in the NeIC Tryggve and Heilsa projects. Read more about FEGA Norway signing.
The Spanish FEGA (es-FEGA) is a national service for storing sensitive biomedical data in Spain. Supported by the Spanish Institute of Bioinformatics (INB) in collaboration with Central EGA, sensitive research datasets are primarily hosted at the Barcelona Supercomputing Centre facilities.
The Swedish Sensitive Data Archive is a secure data archive and sharing platform for sensitive datasets. It was developed by the National Bioinformatics Infrastructure Sweden (NBIS) in collaboration with other Nordic ELIXIR Nodes through the Tryggve and Heilsa projects funded by NeIC and coordinated with Central EGA through ELIXIR. Read more about the Swedish Node signing.
The Swedish Sensitive Data Archive is a secure data archive and sharing platform for sensitive datasets. It was developed by the National Bioinformatics Infrastructure Sweden (NBIS) in collaboration with other Nordic ELIXIR Nodes through the Tryggve and Heilsa projects funded by NeIC and coordinated with Central EGA through ELIXIR. Read more about the Swedish Node signing.
By providing a solution for secure and efficient management of human omics data, the Federated EGA aims to foster data reuse, enable reproducibility, accelerate biomedical research, and improve human health.
Find out more
Interested in setting up your own Federated EGA Node? Check out the FEGA Onboarding Knowledge Base for more information.
The ELIXIR Federated Human Data Community is a great entry point for anyone interested in learning more about the Federated EGA. You can:
- Join the ELIXIR Federated Human Data Community mailing list (select “Human Data”)
- Attend the ELIXIR Federated Human Data Community calls